Big data and Machine learning for PhD in water management with Environment
In-Brief:
- Rain Water Harvesting is the best method to invest the Water, which induces the groundwater levels.
- Big data manipulates and deals with the massive amount of datasets generated via dynamic data that will generate every second.
- Due to many contaminants in the groundwater, the purity of drinking water diminishes its certainty.

Water Management:
71% of the World’s water content is scarce, to 60% due to improper and irresponsible water management. Need not panic about the word Water Management. It stores and preserves the water from rain, kitchens, gardens, and other areas for future purposes. Rain Water Harvesting is the best method to invest the Water, which induces the groundwater levels. It gives double benefits, Increases the water table, and ensures the healthy Environment. Water Management is the stage, where the Ph.D. scholars using Big Data Analytics have an enormous scope to develop the solutions for the crisis.
Recent Ph.D. Research BDA:
To safeguard the Environment and preserve the Water for next-generation, many Researched it in ideal ways.
- The Recent Research Article from Brazil concludes with System analysis models that lend a hand to address and track the variety of water risks and issues all over the World. 1
Big Data:
As the name suggests, Big data manipulates and deals with the massive amount of datasets generated via dynamic data that will generate every second. There are many tools in Big Data to manipulates the data and produce accurate results.
- The work2 proposed that using Big Data and IoT and monitoring the Environment changes, based on differences, will generate the data. These data will be used for analytics purposes.
Machine Learning:
Machine Learning is the Emerging Technology to reduce the complex manipulations and computations by Humans.
The Machine will learn itself according to its source code, what exactly it has to do. Machine Learning implies it’s root on Water Management to reduce the unsolvable manual complexities.
ML possesses its algorithms and techniques for all kind of Data Analytics and Data Science purposes. Some of the familiar algorithms,
- Super-vised Machine Learning algorithms
- Unsuper-vised Machine Learning algorithms
- Artificial Neural Networks
- Badger Prairie Needs Network
- Gradient Boost Regression algorithm
- The proposed article 3 pictures the Water’s quality by remote-sensing in rural areas using Machine Learning algorithms based on image pixels. Those images will be treated as evident data for Data analysis procedures.
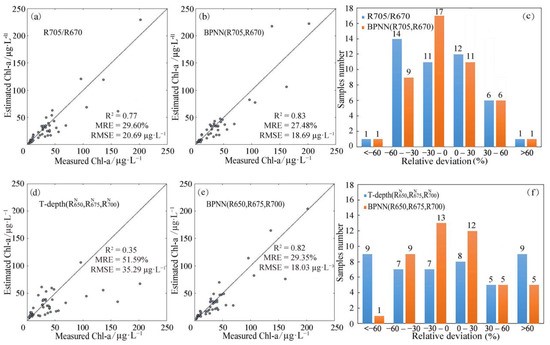
Figure 1. Scatter plot of BPNN model to express the deviations in threats for Water. 3
Big Data In Water Management With Environment:
To kickstarts Farming and improves crop production, a bit of need for technology in it.
- Article 4 proposed the theory of Human-Centered Intelligent Systems to monitor and track the crop’s growth, climatic conditions, pest control, manure rate through sensors and information systems.
- The impact of the Environment in Water Management hits the groundwater levels in the Urban life cycle. The proposed article 5 will resolve the issue of water scarcity due to climatic conditions.
Machine Learning In Water Management:
Due to many contaminants in the groundwater, the purity of drinking water diminishes its certainty.
- The proposed work 6 enhances the originality using the Machine Learning Algorithm XG Boost, ANN, to analyze the groundwater’s purity texture and whether it is legitimate to consume.
- The impact of Anthropogenic activities shakes and hits biodiversity. The deviation and extinction of aquatic biodiversity are due to anthropogenic emissions. The core review of literature 7 is to preserve marine biodiversity using Machine Learning algorithms.
Table. 1 for Big Data and Machine Learning in Water Management:
|
S.NO |
METHOD | REFERENCE | PURPOSE |
| 1 |
System Model Analysis |
[1] |
To analyze and address the variety of water risks |
| 2 |
Radio Frequency Identification |
[2] |
To identify the Environment and climatic conditions |
|
3 |
Badger Prairie Needs Network (BPNN) |
[3] |
To build the estimation models using BDA |
| 4 |
Information systems and Sensors |
[4] |
To detect and predict the crop’s growth |
| 5 |
SCADA, GIS and ESPANET |
[5] |
To ensures the groundwater level |
| 6 |
XG Boost |
[6] |
To speed up the live tracking of purity level of groundwater
|
| 7 | XG Boost and Random Forest | [7] |
To boost the tracking of aquatic biodiversity and cluster according to the species |
Future Scope For Big Data And Machine Learning In Water Management:
BDA and ML have already planted its root deeply. Still, Water Management, Environmental Ethics, Farming, and Agriculture are in hunger to feed with technology. Let’s drive into some future enhancements for BDA and ML in respective fields,
- BDA and ML lend a hand to improve the water utilities, which scrutinize the Customer Service.
EXAMPLE: The intensity of purity can be determined efficiently.
- Data Analytics has a long way to go, but Water preservation doesn’t have the same. Using BDA, we can efficiently predict future climatic conditions and generate the report. Based on the report, further forecasting procedures will be enhanced.
EXAMPLE: Identify the water scarcity region and Magnifies the causation for the scarcity. Put forth an action accordingly.
- Using Machine Learning Algorithms, we can efficiently forecast the project’s cost-effectiveness, which implemented to preserve Water. Every detail will be monitor and control the water level deviations.
EXAMPLE: Comparing with other algorithms, machine learning algorithms produce best results with high accuracy
- Communicating through sensors, forecasting the water levels using Machine Learning algorithms is emerging.
EXAMPLE: To access and analyze the remote-sensing areas will become a tedious one. Like Quarries, Minefields, and Marine areas in such cases, Sensors is mandatory.
Reference:
- Nazli Kosegulu, “A Systems Analysis Approach to Addressing Contemporary Water Challenges: Management Improvements in Brazil and Beyond” (2021).
- Yosra Hajjaji, Wadii Boulila, Imed Riadh Farah, Imed Romdhani, Amir Hussain, Big data and IoT-based applications in intelligent environments
- Bo Jiang, Hailong Liu, Qianguo Xing, Jiannan Cai, Xiangyang Zheng, Lin Li, Sisi Liu, Zhiming Zheng, Huiyan Xu, Ling Meng “Evaluating Traditional Empirical Models and BPNN Models in Monitoring the Concentrations of Chlorophyll-A and Total Suspended Particulate of Eutrophic and Turbid Waters” (2021).
- Ouafiq E., Elrharras A., Mehdary A., Chehri A., Saadane R., Wahbi M. (2021) IoT in Smart Farming Analytics, Big Data Based Architecture. In: Zimmermann A., Howlett R., Jain L. (eds) Human-Centred Intelligent Systems. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 189. Springer, Singapore.
- Inês Figueiredo, Paulo Esteves, Paulo Cabrita, “Water-wise – a digital water solution for smart cities and water management entities, Procedia Computer Science,” (2021).
- Sudhakar Singha, Srinivas Pasupuleti, Soumya S. Singha, Rambabu Singh, Suresh Kumar, “Prediction of groundwater quality using efficient machine learning technique.
- Chemosphere,” (2021)
- Carlotta Valerio, Lucia De Stefano, Gonzalo Martínez-Muñoz, Alberto Garrido, “A machine learning model to assess the ecosystem response to water policy measures in the Tagus River Basin (Spain), Science of The Total Environment,”(2020)



