Bridging the gap of the educational system across different countries through E-Learning
Abstract
The gap in the educational system has been a major drawback globally. The idea and concept of E-Learning have been evolved as a result of many kinds of Research. E-learning has assisted in closing this gap. The main goal of the study is to offer quality education through e-learning by assessing the effectiveness of e-learning mode. The focus has been to assess the e-learning potential to provide a quality education through electronic means and also to evaluate the scope of e-learning. E-learning provides a better standard of living for students across the world. This paper deals with improving the student’s quality of education and their standard of living (Arif Ali, Walayat Hussain, 2011).
Keywords: E-learning environment, e-resources, digital divide, E-Learning, digital Gap, Information Communication Technology (ICT), distance learning, flexible learning.

Introduction
There is an enormous transformation in the field of education due to various researches. Information Technology has provided an innovative learning environment by means of sharing, acquiring and propagating the knowledge to others. E-learning is a method adopted by students for experiencing the teaching sequence, to fulfill their learning tasks, and to achieve the desired results in their learning. However, in many countries, exposure to the e-learning mode is very limited. But, the significance of e-learning has been recognized by many e-learning environments. Information technology can be used to solve this issue (Abuzaid, 2010).

E-Learning
Identifying and preparing for student’s needs and capabilities is the key to success for e-learning. E-learning system must possess these skills to provide suitable methods for learning and appropriate content for users. The data obtained from the student’s profile, type of knowledge, qualities, skills, and personalities can be used to develop an effective E-learning environment for students. The data obtained can be utilized in two ways. The first way is to inform the designers of the e-learning platform about the pedagogy. The second way is to provide a dynamic self-learning ability from the student’s behavior. These learning capabilities will provide long time learning approach. As Artificial Intelligence has the capability of developing and imitating human’s decision-making process, it helps to achieve this learning ability.
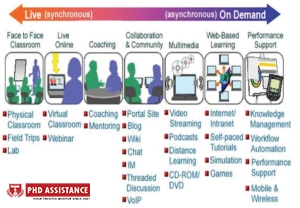
Open Online Courses
This type of learning mode has become a recent trend. This type of learning must mainly offer two features. It must be available to all users at no cost. The main challenge depends on the huge Data Collected from the interactions of students with their learning environments and incorporating them with the AI technologies to create the best e-learning approach. Students are properly Guided According to their needs and their goals and they are motivated so that they can visualize their learning results in the form of graphics. They can also compare their position with their fellow mates (Colchester et al., 2017).
An online learning platform helps to develop an understanding of learning in any environment. E-learning suggests ways for social collaboration and meaningful engagement through education.
Components of E-learning
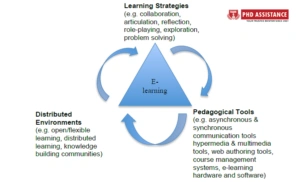
Internet Technologies enable a distributed learning environment to facilitate learning. Three main components in e-learning are:
- Synchronous and asynchronous communication tools.
- Learning strategies in E-learning.
- Distributed environment.
These components form an iterative model, which works collectively to promote a better learning environment. E-learning includes the use of laptops, computers, smartphones, tablets, and some software tools.
There is a gap between education systems between countries. Definitely, there is a limited difference between students’ knowledge about technologies in receiving learning materials through e-mail, voice, and videos. E-learning is found to be the most effective and easily implemented form of education as it is a simpler form of education than the previous model of distance education. As this type of learning has no tutors, no supervision, no cost, e-learning is considered as most effective in bridging the educational gap across countries.
Based on the qualities of online users, there are three approaches that support pedagogical models. The strategies are:
- Exploratory,
- Dialogical, and
- Supportive
Exploratory strategies are theory built based on inquiry-based learning where learners are offered context and they are asked to present solutions, action strategies, and analysis of the situations. The dialogical learning strategies stress on the communication mode by facilitating learners to acquire new knowledge through discussion. Finally, the goal of supportive strategies is to mold the performance and skills by observing and supporting learners while implementing their learning tasks. These strategies are interconnected and improved as a key strategy that supports and promotes other self-directed learning methods as a result of the implementation of all strategies (Tran, 2019).
Conclusion
The most powerful strategy to make students engage in learning activities is through the mode of e-learning. Making students involve actively in education is significant in any Learning Framework such as in-personal learning programs, online classes, and hybrid courses. E-learning mode improves the skills and quality of learning of the students. E-learning also provides full course materials for the entire course thus supporting the learning and teaching methods offered in the classroom (Kim et al., 2019).
Future work
Online content creators must research for an innovative and advanced method that satisfies student’s needs. Further, the research must be done to explore the uncovered areas. Research should be done in the field of learning theories and learner’s association with them as this is significant (Mehta et al., 2019).
References
- Abuzaid, R.A.S. (2010). Bridging the Gap between the E-Learning Environment and E-Resources: A case study in Saudi Arabia. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. [Online]. 2 (2). p.pp. 1270–1275. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877042810002260.
- Arif Ali, Walayat Hussain, and A.A. (2011). E-learning: Closing the digital gap between developed and developing countries. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. [Online]. 5 (11). p.pp. 903–908. Available from: https://www.mendeley.com/catalogue/318b309d-e05a-38de-9ada-5df5d23c1ce6/.
- Colchester, K., Hagras, H., Alghazzawi, D. & Aldabbagh, G. (2017). A survey of artificial intelligence techniques employed for adaptive educational systems within e-learning platforms. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing Research. [Online]. 7 (1). p.pp. 47–64. Available from: https://www.degruyter.com/downloadpdf/j/jaiscr.2017.7.issue-1/jaiscr-2017-0004/jaiscr-2017-0004.xml.
- Kim, H.J., Hong, A.J. & Song, H.-D. (2019). The roles of academic engagement and digital readiness in students� achievements in university e-learning environments. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education. [Online]. 16 (1). p.p. 21. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s41239-019-0152-3.
- Mehta, A., Morris, N.P., Swinnerton, B. & Homer, M. (2019). The Influence of Values on E-learning Adoption. Computers & Education. [Online]. 141. p.p. 103617. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360131519301708.



