Research methodology in biology and life science
INTRODUCTION
Life science is one of the major branches of natural science, the other counterpart being the physical science. Life science or biological science is the scientific study of life and living organisms. Biology falls under the umbrella of natural science discipline and it encompasses various fields such as molecular biology, cell biology, genetics, organismal biology, behaviour health and medicine, neuroscience ecology and evolution. Thus, the research methodology applies to almost all fields in life science and its sub-disciplines.
SUMMARY
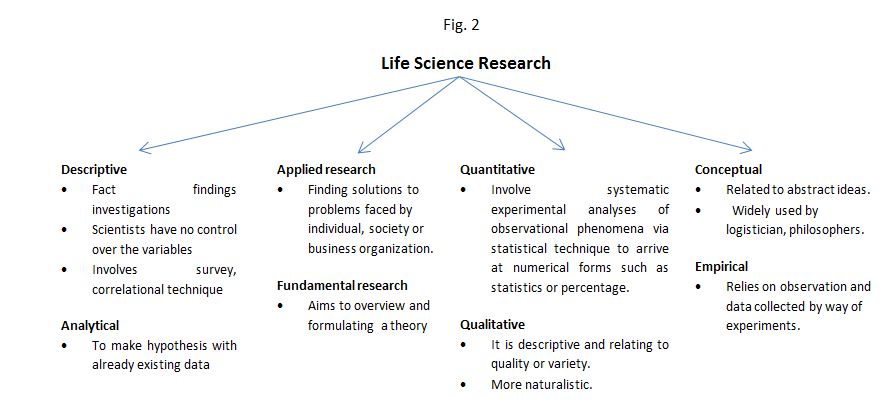
A good and sound research is based on framing a good research question. There are numerous ways of research methodology and it relies on the phenomenon being studied. For any type of research, the first ideal step would be to conduct a bibliographical research which is background reading which helps formulate and test the researcher’s hypothesis. The primary source serves as the most reliable research material. Next, is to do empirical research to verify the hypothesis by obtaining original data through experimentation or observation. Overall, research methodology can be classified as shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2
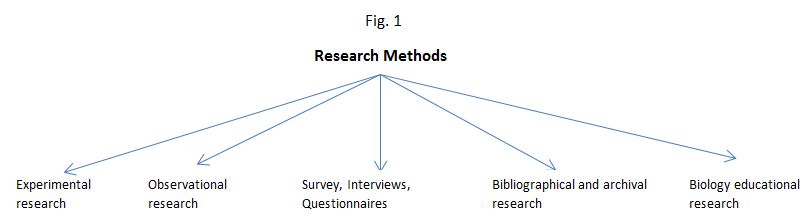
EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH
- The most widely used methodology in life sciences.
- Experiments can be conducted in the field or in laboratory.
- Data may be obtained from cell culture, physiological measurements, biochemical assays, interviews, questionnaires, etc.,
- Emphasizes on quantitative rather than qualitative data.
OBSERVATIONAL RESEARCH
- Often used to generate a question or a hypothesis.
- Also, to test the hypothesis.
- Could be the first step in answering the biological question.
SURVEY, QUESTIONNARIES, INTERVIEWS
- Often used in human biology, phycology, behaviour studies
- To obtain valid results, there must be evidence that subjects respond to items consistently, internal consistency and evidence to prove that the measurements are valid.
BIBLIOGRAPHICAL AND ARCHIVAL RESEARCH
It includes wide range of studies that involve theoretical, interpretive and phenomenological analyses.
BIOLOGY EDUCATION RESEARCH
It compares two different teaching approaches in school children or students in two different groups.
The following steps highlight the guideline to a researcher in completing his research without any confusion:
- Identification of research problem
- Broad literature survey
- Hypothesis formulation
- Preparation of research design
- Determining sample design
- Data collection
- Analysis of data
- Hypothesis testing
- Generalizations and interpretation
- Preparation of the report or presentation of the results
A clearly stated research question helps the researcher to formulate a good study design and good study design is the backbone of any successful research.
- PhD Research Problem Identification in Medical Science - June 4, 2025
- Problem Identification in Computer Science - May 31, 2025
- Five Best Financial service topics - May 24, 2025

