Choosing a Dissertation Methodology: Trends and Influencing Factors
Introduction
Choosing an appropriate research methodology represents a significant decision within the dissertation undertaking. The research methodology ultimately determines how the research questions are examined, how the data are collected, and how the research findings are analysed. Nevertheless, there is limited research focused on what may influence students’ choices of methodology in their dissertations, particularly in education and leadership[1].
The purpose of this article is to examine the existing research on trends in PhD and EdD dissertation methodologies, and to engage in discussion of important factors, which may or may not play some role in selecting a chosen methodology. By knowing the trends in methodologies discussed throughout the article, students can better decide whether to use a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods approach in their dissertation[2].
1. Summary of Dissertation Research Methodologies
Typically, dissertation research falls into one of three, methodological approaches:
📌 Quantitative Research
✔ Based on positivism and is reliant upon statistical analysis[3].
✔ Structured data collection methods are used (e.g., surveys, experiments).
✔ Aims for generalizations that are objective.
📌 Qualitative Research
✔ Based on constructivism and interpretivist philosophy[4].
✔ Data collection uses open-ended approaches (e.g., interviews, case studies).
✔ Gathering data aims to understand non-numerical data with complex social phenomenon.
📌 Mixed-Methods Research
✔ A combination of quantitative and qualitative data collection and analysis[5].
✔ Allows for thorough analysis of data through both numerical data collection and in-depth exploration.
These methodological choices impact depth of research, data analysis and interpretation, and the contribution of a dissertation to the implicit literature[6].
2. Selection of Methodology Trends in Dissertation
2.1 Educational Leadership Dissertations
Lunde et al. (2019) examined educational leadership dissertations to discover the factors predicting students’ choice of methodology. They reviewed 398 dissertations (PhD and EdD) [1] from Virginia and examined the demographic variables of:
✔ Gender
✔ Ethnicity
✔ Age
✔ Religious affiliation
…to see if those demographic variables were related to students’ use of either quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method approaches.
Key Findings:
📌 No statistically significant relationship was found between the demographic variables and students’ choice of methodology[1].
📌 This indicates this measurement of methodology choice was not based on personally identifiable demographics; rather, it may have been influenced by things such as:
- Institutional policies
- Faculty support
- Topic and area of study
2.2 Trend Analysis of Education Dissertations (2007–2017)
To further investigate trends in doctoral dissertation methodology selections, Krueger (2018) examined 130 education-based dissertations from ProQuest Dissertations and Theses database during the years 2007, 2012, and 2017[2].
Key Findings:
📌 A change in trends with respect to doctoral enrolments. More doctoral students were enrolling in EdD programs and fewer in PhD programs.
📌 EdD programs tend to have shorter duration (3 years) than PhD programs (4 years or longer)[2].
In summary, EdD programs are likely gaining traction because of being more applied and shorter in completion time. This desire for a more applied focus and shorter duration might be impacting the methods of research in education[2].
3. The Importance of More Research on Dissertation Methodology Trends
- Future research should:
3.2 Implications for Future Dissertation Research:
📌 By analysing methodology preferences, students can make informed decisions regarding their methodology of study[6].
📌 Universities and other higher education organizations can use studies to craft dissertation guidelines for their program that coincide with the trends of methodology options for higher education[7].
4. Selecting the Appropriate Methodology for Your Dissertation
4.1 Considerations for Choosing a Research Methodology
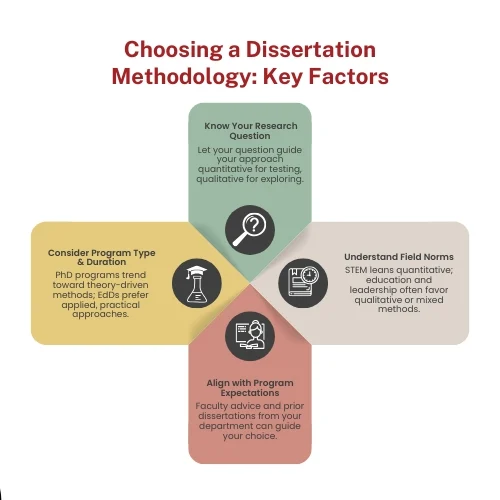
When discerning between quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods, students should ask themselves:
📌 What is my research question?
- Quantitative research is ideally suited if the goal is to test a hypothesis or analyse statistical linkages[3].
- Qualitative research is the best fit if the goal is to study perspectives, behaviour or experiences[4].
- Mixed-methods research may be appropriate if the research is looking for both numerical data and a richer contextual understanding[5].
📌 What methodology is typical of my field?
- Quantitative research will often feature prominently in STEM fields[3].
- Qualitative or mixed methods are more common in social science and education[4].
📌 What is my dissertation advisor or institution’s expectation?
5. Conclusion: Engaging in a Thoughtful Methodology Decision-Making Process
It is important for students in a doctoral program to know what types of dissertation methodology trends exist. This review of studies indicates that while student demographics are not the major factor impacting decision-making on methodology use, there are other factors that make substantial impacts, such as:
✔ The type of doctoral program (PhD vs. EdD)
✔ The institutional research culture
✔ The focus of the dissertation (practical vs. theoretical)
… all heavily impact dissertation methodology decisions, and student outcomes.[1][2][3] Through judicious consideration of their research objectives, their academic discipline, and the expectations of their program; students can identify which methodology will work best for them and establish a scholar-practitioner foundation for their dissertation, allowing for success throughout their doctoral journey. Be informed by the trends, the expectations of professors, and the goals of the research to make an informed decision. Don’t wait to start working on a draft of your methodology, if you want to write a successful dissertation!

